Urinary tract infection

A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection of the urine usually caused by a bacteria germ. Urine should not have any germs at all.
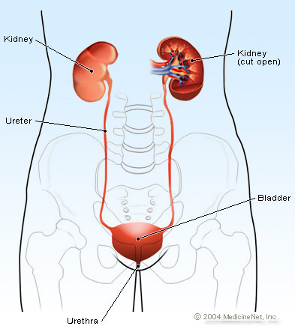
Urine is made in the two kidneys (one on the left, one on the right) and travels down the ureters to the bladder, which acts like a temporary storage drum. The urine then goes out through the urine tube or urethra and into the toilet!
Most commonly, germs get into that urine tube/urethra and then travel upward into the bladder and can even go as far as the kidneys. Kidney infections can be serious because scarring can cause huge problems like kidney failure; and if the infection gets in the blood stream, sepsis.
Who gets a UTI
Both men and women get UTIs, but they are far more common in women.
Why? Because of how God designed our bodies – everything “down there” is so close and germs get into the urine tube/urethra very easily.
In fact, some women are plagued with UTIs especially after sex – honeymoon cystitis, after using a hot tub, holding pee for too long, and if not super-careful about wiping the vaginal and rectal areas, etcetera.
Although a UTI can happen out of the blue, there are certain situations that tend to predispose persons to getting one:
- Blockage or obstruction anywhere in the urine tract – Kidney and bladder stones, strictures, enlarged prostate
- Catheter
- Poor immune system – Diabetes Mellitus, HIV, Cancer, certain medications
- Pregnancy
SYMPTOMS OF A UTI
The urine is usually foul smelling (wrenk!), cloudy or may even contain blood.
What you may feel depends on where in the tract the infection is located.
Lower UTIs (bladder, urethra) tend to cause:
- Burning on urinating
- Passing urine very frequently
- Having the constant urge to go; sometimes very little or no urine comes
- Cramps in the lower abdomen or lower back, feeling bloated, the bladder feels full
Upper UTIs (kidneys) typically cause:
- Back pain
- Fever
- Chills and rigors
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Lethargy and weakness
If the UTI is caused by a sexually transmitted infection (STI), there may be a vaginal or penile discharge as well.
Beware: STIs can also cause UTI symptoms.
Men – may feel pain in the bottom (rectal) or even in the balls/testicles.
Babies – may have poor feeding, vomit, changing diapers more often, irritability, diarrhea, fever, etc.
Middle aged women – incontinence, the inability to hold up the urine, may be their only symptom.
Elderly – may have no symptoms at all! Sudden confusion (for no apparent reason), weakness and lethargy may be the only clues to a possible UTI in the elderly.
TREATMENT
As soon as they feel these symptoms, many people drink lots of water, take vitamin c rich foods or pills, pineapple and cranberry juice. In my experience, this is NOT very effective. Those measures are useful to prevent a UTI.
Once an infection is present, antibiotic treatment is usually necessary. The longer you wait, the worse it gets!!
Beware: Urine infections travel up towards the kidneys where they can cause permanent damage if untreated.
What your doctor will do
- Check your vitals, temperature, and urine
- Examine your abdomen, etc
- She/he may order tests: urine tests to look for the germ and antibiotics that will readily kill the bacteria (Urine Culture and Sensitivity) and an ultrasound if kidney infection or swelling of the kidney is suspected.
How is a UTI treated
- Use of antibiotic to kill the bacteria germs and help you with the pain and discomfort
- Acetaminophen (panadol) and ibuprofen (advil) will help with the pain
- Antispasmodics like baralgin are effective for the cramping and frequency
Completing the entire course of the antibiotic is important because germs can develop resistance if you don’t.
The medicine used will depend on how severe the infection is and where it is.
For example,
- A bad kidney infection will need IV antibiotics that is, in the vein/drip
- A simple bladder infection can usually be successfully treated with oral antibiotics
- A UTI due to a sexually transmitted infection may need more than one antibiotic
- In pregnancy, some antibiotics should not be used
If there is an underlying cause, it needs to be dealt with. For example, kidney stones may require a referral to the urologist. An indwelling catheter will need to be replaced.
PREVENTION
- Drinking lots of water to flush the urinary tract
- Don’t refrain from urinating for long periods
- Women – wiping from front to back
- Men – retracting foreskin
- Washing area before sex and urinating after sex
- Avoiding hot tubs
- Avoid things that can irritate the urethral area – tight clothes, bubble baths, douche, feminine products
- Cotton underwear is best as they wick away urine drops.
MOVING FORWARD WITH A UTI
Both adults and children generally do very well with treatment.
If left untreated, complications such as kidney failure, dehydration, abscess, strictures can ensue.
However, if a UTI is not detected early, it may be disastrous (even fatal) in the elderly. Untreated UTIs in pregnancy are associated with premature delivery and low birth weight infants.
Serving God and the elderly are two of Dr. Jennice Baker’s passions. A house call doctor and health educator, she has been a Christian from her youth.